Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept in medicine. It has already become a practical, daily reality that influences nearly every corner of healthcare. From radiology labs to hospital administration, from remote monitoring to drug development, AI is shifting how patients, doctors, and health systems interact.
As of 2025, the role of AI is no longer confined to isolated pilot projects. Instead, AI systems are embedded into workflows, trusted by clinicians, and even expected by patients. The global healthcare sector faces pressures like aging populations, chronic illnesses, rising costs, and workforce shortages. AI offers both relief and reinvention. This article takes a deep dive into AI’s impact on healthcare, updated with the latest 2025 insights, research, and case studies.
We’ll explore why AI matters, which technologies drive it, real-world applications, benefits and risks, emerging market trends, and the future outlook. Whether you are a clinician, administrator, policymaker, or simply a curious reader, this guide is written to be clear, engaging, and useful.
Why AI Matters in Healthcare
Healthcare is under strain. Populations are aging, chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease are rising, and global pandemics remain a threat. At the same time, many healthcare systems face burnout among clinicians, shortages in nursing, and increasing operational costs. AI is emerging as a vital partner in solving these problems.
A 2025 AMA survey revealed that 66% of physicians now use some form of AI in practice. That is nearly double the rate from just two years ago. Notably, 68% said AI had already improved patient care.
So why is AI so important? The answer lies in efficiency and accuracy. Humans cannot process terabytes of health data at once, but AI can. Algorithms can analyze complex images, identify tiny anomalies, or predict future risks with precision. AI can also automate time-consuming administrative tasks that consume up to 40% of a doctor’s workweek.
Equally important, AI makes healthcare more equitable. Remote AI tools and mobile apps allow patients in rural or underserved areas to access expertise that was once restricted to major hospitals.
In short, AI is not about replacing clinicians. It is about amplifying their ability to do more, faster, and better.

Core AI Technologies in Healthcare
AI is not one technology but many, working together. Here are the major pillars powering healthcare innovation in 2025:
- Machine Learning (ML) & Deep Learning (DL): These systems train on large datasets to recognize patterns, classify inputs, and make predictions. They power diagnostic imaging and risk prediction.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Generative AI: These tools understand and generate human language, allowing them to summarize reports, draft medical notes, or answer patient questions.
- Multimodal AI: Models that analyze several types of data—for example, combining X-rays, lab results, and genetic data to provide a fuller picture.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): Systems that learn by trial and error, improving over time. RL is showing promise in treatment optimization, especially in intensive care.
- Agentic AI & Autonomous Agents: New in 2025, these AI systems can act semi-independently, scheduling appointments, coordinating lab results, or flagging issues in workflows.
- Explainable AI (XAI): A growing necessity. Clinicians need to understand why an AI made a decision, especially when lives are at stake.
Together, these technologies are moving healthcare toward a future where human expertise and machine intelligence work hand in hand.
Key Real-World Applications & Use Cases
1. Diagnostic Imaging & Radiology
Radiology has been one of the first fields to benefit from AI. Algorithms can now analyze medical images with remarkable precision. In mammography, for example, AI-assisted systems in 2025 detected nearly 30% more breast cancers than standard methods. The advantage is not just in accuracy but also in speed. A scan that might take a radiologist 20 minutes to interpret can be flagged by AI in under 30 seconds.
AI is also reducing diagnostic fatigue. Radiologists review hundreds of images daily, increasing the risk of oversight. AI serves as a second reader, improving both safety and confidence.
2. Clinical Decision Support & Evidence Summaries
Medicine evolves quickly. Thousands of studies are published each week. Clinicians cannot possibly read them all. AI decision support systems scan, summarize, and extract the most relevant insights. Some AI assistants can even cross-reference a patient’s history with the latest guidelines and suggest treatment options.
This means care decisions are more evidence-based and less dependent on incomplete knowledge. Doctors remain in control, but AI equips them with sharper tools.
3. Automated Documentation & Medical Scribes
One of the biggest pain points in healthcare is documentation. Studies suggest doctors spend nearly half their day on paperwork. AI-powered scribes now record conversations, summarize visits, and enter notes directly into electronic health records.
By 2025, major health systems report that AI scribes reduce documentation time by 60%. This not only boosts efficiency but also improves patient experience because doctors can maintain eye contact and focus fully during consultations.
4. Remote Monitoring, Wearables & Virtual Care
AI-driven wearable devices are becoming mainstream. Smartwatches, glucose monitors, and heart rhythm trackers can now alert clinicians to risks before a crisis occurs. For example, an AI system monitoring cardiac patients can predict the likelihood of a heart attack days before symptoms appear.
Hospitals are also experimenting with “virtual wards,” where patients recover at home but are monitored through connected devices. AI interprets the data and notifies clinicians if intervention is needed. This reduces hospital stays and costs.

5. Drug Discovery & Biotechnology
Traditional drug discovery can take over a decade and billions of dollars. AI is slashing these timelines. By simulating molecular structures and predicting how compounds will behave, AI helps scientists find promising candidates faster.
In 2025, industry analysts estimate that nearly a third of all new drugs in development rely on AI assistance. This not only accelerates progress but may also lower drug prices for patients.
6. Claims, Billing & Administration
Administrative costs drain healthcare budgets. AI helps streamline coding, billing, and claims processing. Automated systems can detect errors, flag fraud, and speed up approvals. For patients, this means fewer billing surprises and faster reimbursements.
7. Population Health & Prevention
AI is not just about individual care. It is also reshaping public health. Algorithms can predict disease outbreaks, guide vaccination campaigns, and identify communities at higher risk for chronic conditions. On an individual level, AI risk calculators now predict susceptibility to diseases decades before symptoms appear.
8. Agentic Systems & Autonomous Agents
Hospitals in 2025 are piloting AI “agents” that operate semi-autonomously. For example, an AI agent may automatically schedule lab work, send reminders, or coordinate specialists. While still early, these systems represent a shift toward proactive, automated healthcare operations.
Benefits, Challenges & Ethical Risks
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
- More efficient workflows and reduced administrative burden
- Higher diagnostic accuracy and earlier disease detection
- Personalized treatment recommendations
- Lower costs and better scalability
- Expanded access for underserved populations
- Relief for overworked staff, reducing burnout
Challenges and Risks
- Bias in data: If training data lacks diversity, AI may perpetuate health inequalities.
- Transparency: Clinicians need to know why AI made a choice.
- Regulatory gray areas: Liability is unclear when AI makes mistakes.
- Integration hurdles: Many tools never progress beyond the research phase.
- Overreliance: Doctors risk losing diagnostic sharpness if they depend too heavily on AI.
- Privacy and security: Patient trust requires strong safeguards.
- Equity concerns: Communities underrepresented in data sets may receive lower-quality predictions.
The lesson: AI should not replace humans. Instead, it should extend human capacity while maintaining accountability.
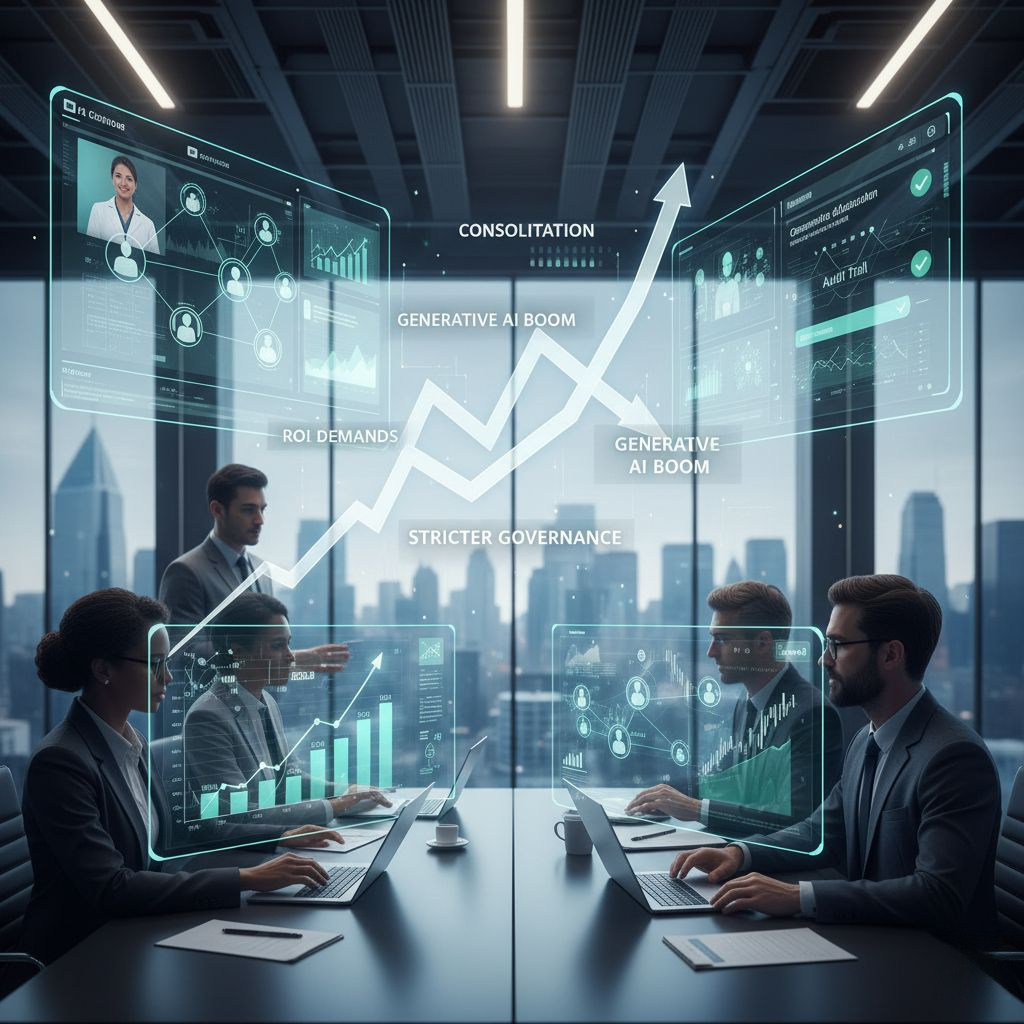

AI & Market Trends in 2025
Healthcare AI is not just advancing scientifically. The business landscape is shifting too.
- Consolidation: Startups are merging with larger firms to provide end-to-end solutions.
- ROI demands: Hospitals now expect clear savings and measurable outcomes before investing.
- Generative AI boom: Beyond chatbots, generative AI now drafts medical notes, creates patient education content, and even models clinical trial outcomes.
- Stricter governance: Regulators demand explainability, audit trails, and clinician oversight.
- Agentic AI rise: 2025 is being called the “year of healthcare agents,” as systems take on proactive roles.
Future Outlook & What’s Next
Looking forward, several trends are emerging:
- Reinforcement Learning expands: Instead of just predicting risks, AI will recommend and adapt treatments in real time.
- Multimodal models mature: By combining images, genetics, and history, these systems will give richer insights.
- Regulatory standards strengthen: Expect clearer laws around liability, fairness, and interoperability.
- Global accessibility improves: Lightweight AI systems will help low-income regions.
- Human-AI collaboration becomes standard: The future is not man vs. machine, but man with machine.
Key Takeaways
- AI in healthcare has shifted from promise to practice.
- Radiology, drug discovery, documentation, and prevention are leading applications.
- The greatest opportunities lie in efficiency, accuracy, and access.
- Risks like bias, privacy, and liability must be managed.
- Market adoption now demands ROI, ethics, and trust.
- The future is collaborative: AI supports, humans lead.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will AI replace doctors?
No. AI is a tool to enhance decision-making, not to replace human empathy and judgment.
Is AI safe in healthcare?
Yes, when validated, monitored, and overseen. The risk is misuse or poor implementation.
How accurate is AI?
Accuracy varies. In radiology and dermatology, AI can match or exceed human performance. In other areas, results are mixed.
Can smaller clinics use AI?
Yes. Cloud platforms and modular tools make AI more accessible than ever.
When will AI be standard in hospitals?
It is already standard in imaging, coding, and documentation. Broader use depends on investment and governance.
Conclusion
AI’s role in healthcare is no longer experimental. In 2025, it is operational, measurable, and growing. The industry is at a crossroads: those who adopt responsibly will see major improvements in efficiency and patient care. Those who delay may struggle to keep up.
If you are part of a healthcare organization, here are the next steps:
- Align AI strategy with patient outcomes.
- Start with pilots in safe, high-value areas.
- Invest in explainability, oversight, and clinician training.
- Monitor outcomes continuously.
- Scale carefully, building trust at every stage.
The promise of AI in healthcare is real, but its future depends on careful, ethical, and strategic adoption.